Motion Layout vs Constraint Layout in Android Knowing deeper
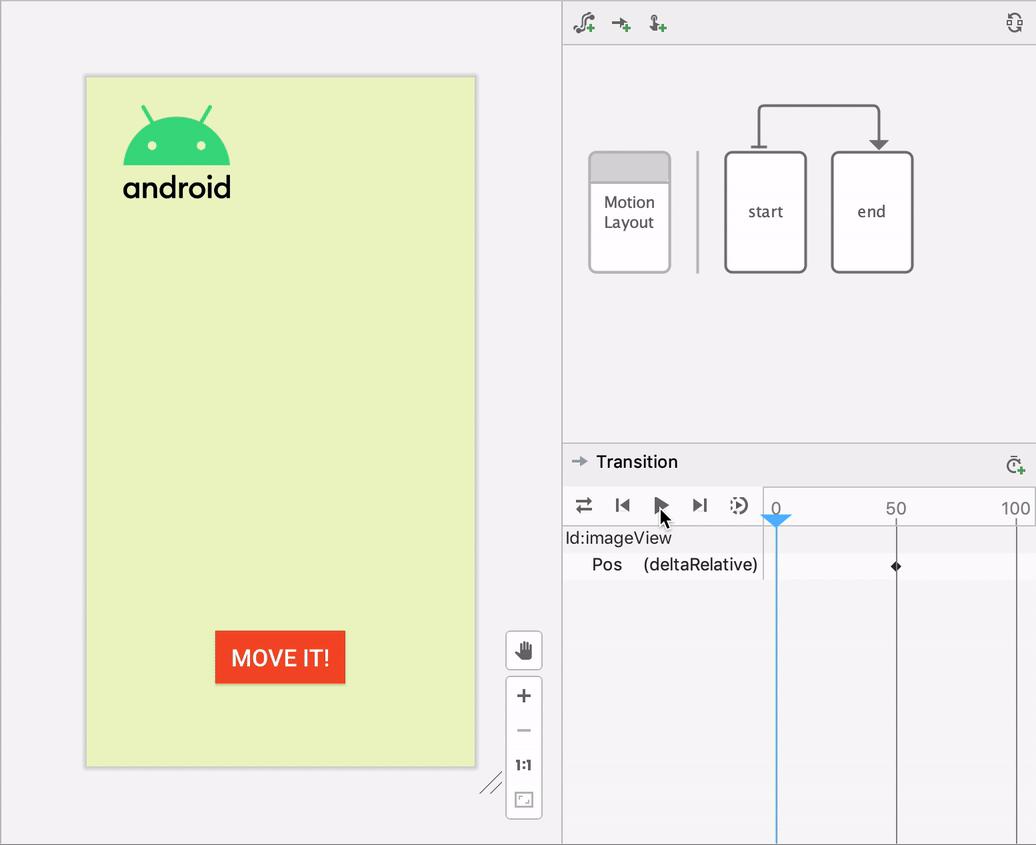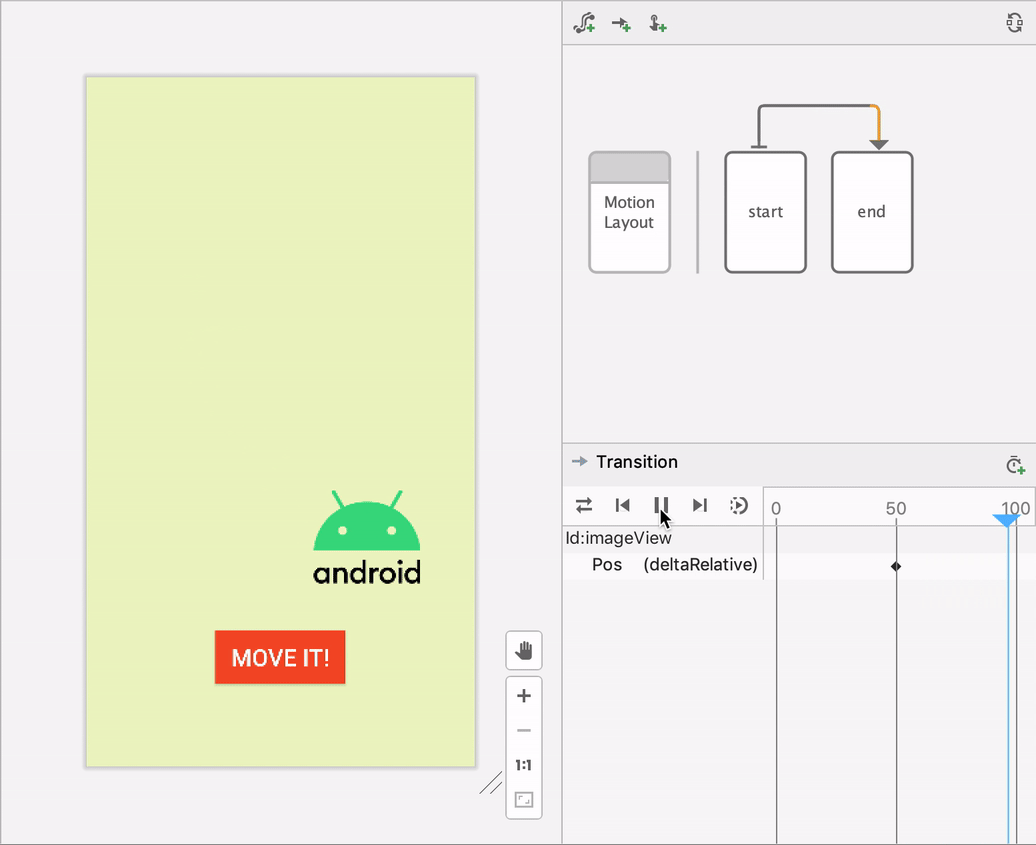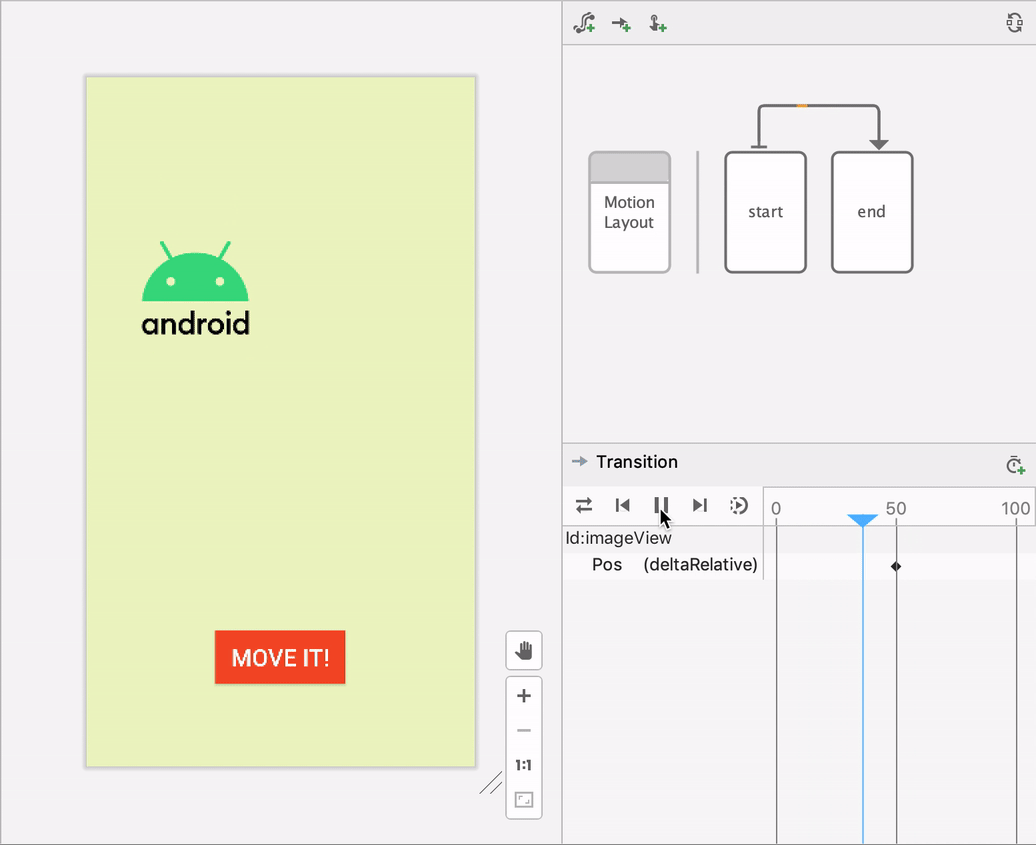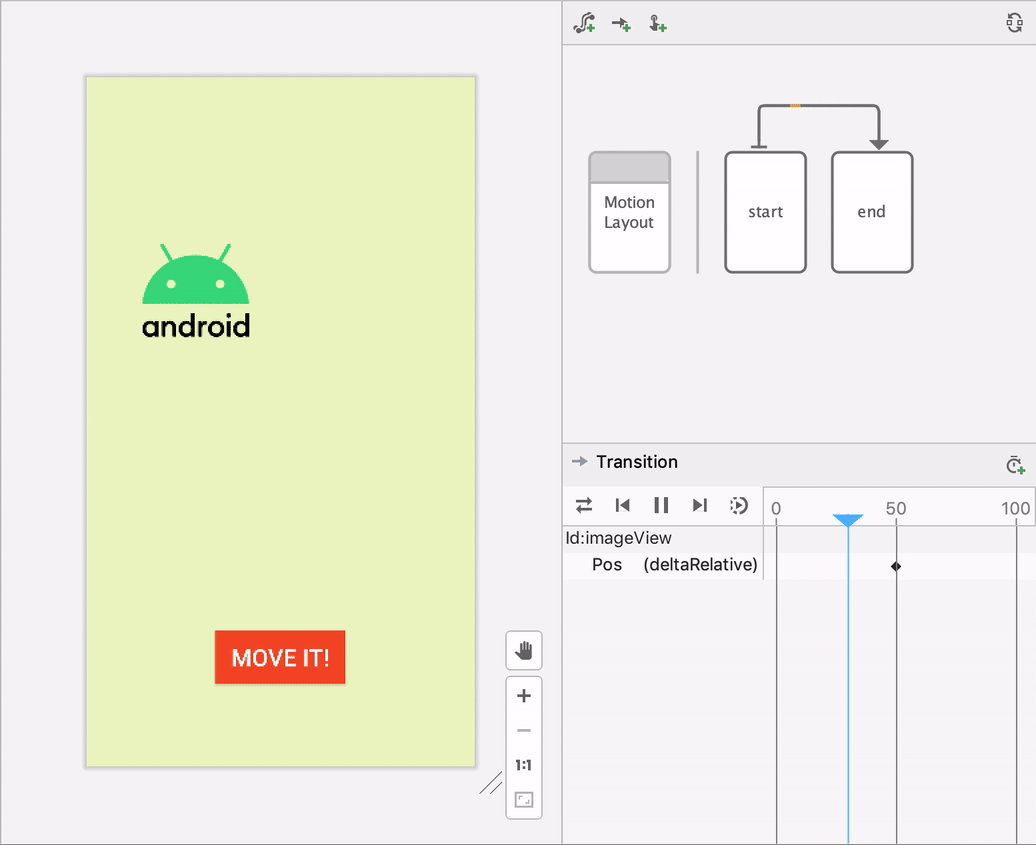
Motion Layout
Everything you do in Constraint Layout you can do also in Motion Layout. We use it especially for animation. Swiping, interactions with different objects, fading in out, spinning, ecc.Constraint Layout
It helps to create UI lot faster and easier.Constraint : A connection or alignment to another UI element to the parent layout, or to an invisible guideline.
Advantages of Constraint Layout
- you can make it responsive to screens and resolutions
- usually flatter view hierarchy
- optimized for laying out its view
- free-form - place views anywher, and the editor helps to add constraints
Constraints
- Absolute Positioning : positioning in numerical, such as position in x, y coordinates
- Relative Positioning : views are positioned by specifying relationship to other views.
- Fixed Constraint : A constraint that is specified sing a hard-coded number. Ex. margin
- Adaptable Constraint : A constraint that defines a relationship in relative and weighted terms.
Ratio
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="0dp" app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="2:1" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/box_one_text" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" android:text="Ratio Button " />Here the button will be Twice the wide as the height. 2:1
Comments
Post a Comment